If you’ve been hearing about Solana and its impressive capabilities, it’s time to dive into the underlying mechanics that make it so groundbreaking. Solana, a cryptocurrency that aims to improve upon Ethereum, implements a proof-of-history consensus mechanism that revolutionizes traditional blockchain technology. By utilizing timestamps to define blocks, Solana ensures accurate and secure transactions. What sets it apart is its clever combination of proof of history and delegated proof of stake, enabling faster computations and addressing the scalability issues that plague other platforms. With faster transaction speeds and lower costs, Solana’s SOL token, readily available on major exchanges, offers a promising avenue for seamless transactions on the Solana network.

The Basics of Solana’s Proof-of-History Consensus Mechanism
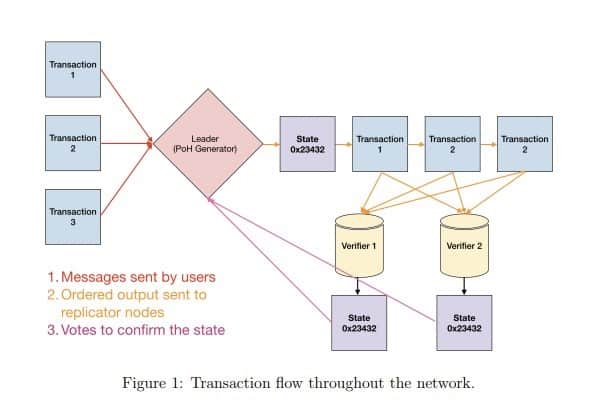
Solana (SOL) is a cryptocurrency that aims to enhance the functionality and scalability of Ethereum. One of the most critical aspects of Solana’s architecture is its unique consensus mechanism called Proof-of-History (PoH). This mechanism utilizes timestamps to define blocks in the blockchain, effectively improving the efficiency and reliability of the network.
How Solana’s Proof-of-History Consensus Mechanism Works
In traditional blockchain networks, achieving consensus on the order of transactions is a complex and time-consuming process. Solana’s PoH takes a different approach by introducing a verifiable delay function (VDF), which cryptographically associates a timestamp with each block.
The PoH algorithm creates a historical record of all events by generating a unique Proof-of-History for each new transaction or block. This record is stored in a sequential format, allowing validators to quickly verify the timestamps and order of events.
By using a sequential Proof-of-History, Solana achieves a significant advantage in terms of scalability and throughput. Validators can quickly process transactions, and the network can handle a high volume of transactions per second, making it ideal for applications that require fast and secure computations.
The Role of Timestamps in Solana’s Consensus Mechanism
Timestamps play a crucial role in Solana’s PoH consensus mechanism. Each new block is linked to a previous block through its timestamp, creating a time-based dependency. This ensures that the blocks are ordered correctly and prevents any potential manipulation or tampering.
The use of timestamps also allows for the easy verification of block order, as validators can quickly compare the timestamps of different blocks. This efficient verification process contributes to the overall speed and scalability of the Solana network.
Advantages of Using Proof-of-History in Solana
Solana’s Proof-of-History consensus mechanism provides several advantages over traditional consensus algorithms:
- Increased Scalability: The PoH mechanism allows Solana to handle a large number of transactions per second, making it highly scalable. This is crucial for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and other high-demand use cases.
- Efficient Verification: The PoH algorithm ensures fast and efficient verification of block order and transaction history. Validators can easily confirm the validity of new blocks, enhancing the security and reliability of the network.
- Reliable Timestamps: The use of timestamps in Solana’s PoH algorithm creates a trustable time-based dependency, preventing manipulation or tampering with the order of blocks.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Compared to proof-of-work (PoW) algorithms, Solana’s PoH mechanism consumes significantly less energy. This makes it more environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- Enhanced Security: By combining the advantages of both PoH and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), Solana provides a robust and secure environment for computations and transactions.
Overall, Solana’s PoH consensus mechanism offers a novel approach to achieving consensus in blockchain networks. Its efficient use of timestamps, scalability, and enhanced security make it a promising platform for various applications and use cases.
Understanding Solana’s Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) Mechanism
In addition to the Proof-of-History consensus mechanism, Solana utilizes a Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) mechanism. This mechanism further enhances the scalability and security of the Solana network by balancing the responsibilities between two main roles: delegators and validators.
Overview of Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
Delegated Proof-of-Stake is a consensus mechanism commonly used in blockchain networks. It allows token holders to delegate their voting power to trusted validators, who are responsible for maintaining the network and validating transactions.
In Solana’s DPoS mechanism, token holders can delegate their SOL tokens to validators of their choice. These validators play a crucial role in block creation and transaction validation. By delegating tokens, participants in the network can actively contribute to the consensus process and help secure the network.
The Role of Delegators and Validators in Solana’s DPoS
Delegators in Solana’s DPoS mechanism hold SOL tokens and have the power to choose and delegate their tokens to validators. By delegating tokens, they entrust the chosen validator with the responsibility of maintaining the network’s security and ensuring transaction validity.
Validators, on the other hand, are responsible for validating transactions, creating new blocks, and maintaining the overall network integrity. Their role includes verifying the PoH timestamps, ensuring the correctness of transactions, and preventing potential attacks or manipulations on the network.
The combination of the Proof-of-History and DPoS mechanisms allows Solana to achieve a high level of decentralization, scalability, and security. Delegators and validators work together to maintain the network’s integrity and validate transactions efficiently.
Comparison of Solana’s DPoS and Other Consensus Mechanisms
Solana’s DPoS mechanism offers several advantages over other consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS):
- Scalability: DPoS allows Solana to process a high number of transactions per second, making it highly scalable. This is crucial for applications that require fast and efficient transactions.
- Energy Efficiency: Unlike PoW mechanisms, which require extensive computational power and energy consumption, DPoS significantly lowers the energy requirements of the network. This makes Solana a more environmentally friendly blockchain platform.
- Decentralization: DPoS achieves a balance between decentralization and efficiency. While validators play a crucial role in maintaining the network, the delegation of voting power ensures that token holders actively participate in the consensus process.
- Cost-effectiveness: DPoS eliminates the need for expensive mining equipment and resources, making participation in the Solana network more accessible and cost-effective for validators and delegators.
Solana’s DPoS mechanism, coupled with the Proof-of-History consensus mechanism, provides a unique blend of scalability, security, and efficiency, making it an attractive choice for various decentralized applications.
Scalability and Speed in Solana
Scalability is a fundamental concern for blockchain networks, especially as the demand for decentralized applications and transactions continues to grow. Solana aims to address scalability issues by incorporating innovative solutions and technologies into its architecture.
How Solana Addresses Scalability Issues
Solana tackles scalability challenges through a combination of its consensus mechanisms, network design, and advanced technologies. Its Proof-of-History mechanism, coupled with DPoS, allows for rapid transaction processing and efficient block creation, ensuring that the network can handle a high volume of transactions.
Additionally, Solana implements a technique called Tower BFT, which enhances network throughput and responsiveness. Tower BFT is a consensus algorithm that enables validators to quickly reach agreement on the validity of blocks.
By incorporating these mechanisms and technologies, Solana can achieve high scalability, making it suitable for decentralized applications that require fast and efficient transactions.
Faster Transaction Speeds in Solana
Transaction speed is a critical factor for blockchain networks, as it directly impacts the user experience and the applicability of the technology in real-world scenarios. Solana’s architecture enables extremely fast transaction speeds, making it well-suited for use cases that require near-instantaneous transaction confirmation.
The combination of Proof-of-History, DPoS, and Tower BFT allows Solana to process a high number of transactions per second (TPS). The network has consistently demonstrated speeds of over 65,000 TPS, surpassing the capabilities of many other blockchain platforms.
This high transaction speed opens up possibilities for various applications, including decentralized finance, gaming, and high-frequency trading, where fast and reliable transactions are crucial.
Lower Transaction Costs in Solana
Transaction costs, often referred to as gas fees, have been a point of concern in many blockchain networks, especially as transaction volumes increase. Solana’s architecture addresses this issue by significantly reducing transaction costs, making it more accessible and cost-effective for users.
The efficient consensus mechanisms and scalability features in Solana contribute to lower transaction costs. With high transaction throughput and low fees, Solana becomes an attractive platform for applications that require frequent and affordable transactions.
Lower transaction costs have a positive impact on user adoption and can fuel the growth of decentralized applications and the overall Solana ecosystem.
Security Considerations in Solana
Security is a paramount concern for any blockchain platform, as it directly impacts the trust and reliability of the network. Solana incorporates several security measures to ensure the integrity and robustness of its blockchain.
The Security Benefits of the Proof-of-History Mechanism
Solana’s Proof-of-History (PoH) mechanism plays a significant role in enhancing the security of the network. By cryptographically linking blocks through timestamps, PoH prevents tampering and manipulation of the order of transactions.
The sequential nature of PoH enables quick and efficient verification of block order, ensuring the integrity of the blockchain. Validators can easily detect any attempts to manipulate the timestamps or alter the order of transactions, enhancing the overall security of the network.
How Solana’s DPoS Enhances Security
Solana’s Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) mechanism further enhances the security of the network by fostering decentralization and active participation. DPoS allows token holders to delegate their voting power to validators, enabling broad representation and distributed decision-making.
The delegation process in DPoS ensures that the responsibility of maintaining the network and validating transactions is shared among multiple validators. This distributed approach minimizes the risk of a single point of failure and provides the opportunity for continuous monitoring and oversight.
Additionally, the economic incentives provided by DPoS encourage validators to act honestly and responsibly, as any malicious behavior or misconduct can result in losing their reputation and stake.
Challenges and Potential Risks in Solana’s Consensus Mechanism
While Solana’s consensus mechanisms offer several advantages in terms of scalability, speed, and security, there are also potential challenges and risks that need to be considered.
One potential challenge is the reliance on a small number of validators in the DPoS mechanism. While Solana aims to maintain decentralization through the delegation process, the concentration of voting power in a few validators can raise concerns about network vulnerability if collusion or compromise occurs.
Another consideration is the rapid pace of technological advancements and potential vulnerabilities that may arise. As the Solana ecosystem evolves, it is crucial to stay vigilant and implement robust security measures to mitigate any emerging risks.
Continuous research, audits, and community engagement are essential to address these challenges and ensure the long-term security and stability of the Solana blockchain.

Comparing Solana to Ethereum and Cardano
Solana’s unique blend of innovative consensus mechanisms, scalability solutions, and high-performance features sets it apart from other blockchain platforms such as Ethereum and Cardano. Let’s take a closer look at some key points of comparison.
Transaction Speeds and Costs in Solana, Ethereum, and Cardano
When it comes to transaction speeds, Solana outshines Ethereum and Cardano. Solana’s ability to process over 65,000 transactions per second (TPS) far surpasses Ethereum’s current TPS of around 15. In comparison, Cardano currently supports approximately 250 TPS.
In terms of transaction costs, Solana offers significantly lower fees compared to Ethereum, which has been plagued by high gas fees during periods of high network congestion. Cardano, on the other hand, aims to minimize transaction costs through its unique approach to transaction validation.
Scalability Differences Between Solana, Ethereum, and Cardano
Scalability is a critical factor for blockchain platforms, especially as demand increases. Solana’s architecture and consensus mechanisms give it a significant advantage in scalability over Ethereum and Cardano.
Ethereum’s current scalability limitations have led to congestion and delays during peak usage, affecting the user experience and hindering the growth of decentralized applications. Cardano has implemented several scalability features such as sharding to address this limitation, but it is still in the early stages of implementation.
On the other hand, Solana’s focus on scalability through the combination of PoH, DPoS, and Tower BFT enables it to handle a high volume of transactions without compromising speed or efficiency.
Advantages of Solana over Ethereum and Cardano
Solana offers several advantages over Ethereum and Cardano:
- Speed and Scalability: Solana’s ability to process a high number of transactions per second and its efficient consensus mechanisms position it as a superior choice for applications that require fast and scalable transactions.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Solana’s architecture results in significantly lower transaction costs compared to Ethereum, making it more accessible and cost-effective for users.
- Robust Security: The combination of PoH and DPoS enhances the security of Solana’s network, ensuring the integrity and reliability of transactions and computations.
- Developer-Friendly: Solana offers a developer-friendly environment and a rich ecosystem of tools and resources for building decentralized applications and smart contracts.
While Ethereum and Cardano have their own strengths and unique features, Solana’s performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness make it a worthy alternative for developers and users seeking fast and scalable blockchain solutions.
Use Cases and Applications of Solana
Solana’s unique features and capabilities open up a wide range of use cases and applications in the blockchain ecosystem. From decentralized finance (DeFi) to smart contract development, let’s explore some potential areas where Solana excels.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) on Solana
Decentralized finance (DeFi) has gained significant traction in recent years, providing users with unprecedented access to financial services and products. Solana’s high transaction speeds, low costs, and secure infrastructure make it an excellent platform for various DeFi applications.
With Solana, users can efficiently trade tokens, provide liquidity, and participate in yield farming and lending protocols. The platform’s scalability ensures that DeFi applications on Solana can handle a high volume of transactions without congestion, improving the overall user experience.
Smart Contract Development on Solana
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that allow the automation of agreements and transactions. Solana provides a robust environment for developing and deploying smart contracts, opening up possibilities for various industries and applications.
Developers can leverage Solana’s developer-friendly ecosystem and tools to create complex and scalable smart contracts. The platform’s high-performance capabilities and low transaction costs make it an attractive choice for deploying smart contracts that require fast and efficient execution.
Other Potential Applications on Solana
Beyond DeFi and smart contracts, Solana’s scalability and speed make it suitable for a wide range of applications, including but not limited to:
- Supply Chain Management: With its fast transaction speeds and secure infrastructure, Solana can enhance transparency and efficiency in supply chain operations, helping to prevent fraud and track goods.
- Gaming and NFTs: Solana’s high throughput and low latency make it ideal for gaming applications and the creation and trading of non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
- Real-Time Data Processing: Solana’s ability to handle a large volume of transactions in near real-time makes it well-suited for applications that require real-time data processing, such as IoT and sensor networks.
The versatility of Solana, coupled with its speed, scalability, and security, makes it an attractive blockchain platform for a wide range of use cases and applications.
Obtaining and Using the SOL Token
The SOL token is the native cryptocurrency of the Solana network, and it plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Here’s how you can obtain and utilize SOL tokens.
Purchasing SOL on Major Exchanges
SOL tokens can be purchased on major cryptocurrency exchanges that support Solana. These exchanges provide a platform for users to buy and sell SOL tokens using other cryptocurrencies or fiat currency.
When purchasing SOL tokens, it is essential to choose a reputable and secure exchange platform. Conduct thorough research and follow best practices for cryptocurrency exchanges to ensure the safety of your funds.
Using SOL for Transactions on the Solana Network
SOL tokens are used for transactions, smart contract execution, and participation in the Solana network. Users can utilize SOL tokens to pay for transaction fees, interact with decentralized applications, and execute various operations within the Solana ecosystem.
To use SOL tokens, users need to have a Solana-compatible wallet. These wallets enable users to store, manage, and transfer their SOL tokens securely.
Storing and Securing SOL Tokens
Storing and securing SOL tokens is vital to protect your investment and assets. There are different types of wallets available for storing SOL tokens, including:
- Hardware Wallets: Hardware wallets, such as Ledger and Trezor, offer a high level of security by storing the private keys offline. These wallets are considered one of the safest options for storing cryptocurrencies.
- Software Wallets: Software wallets, such as Solana’s official wallet or other compatible wallets like Trust Wallet and Atomic Wallet, are apps or software that can be installed on your computer or mobile device. They provide a convenient way to store and access your SOL tokens.
When using any type of wallet, it is essential to follow best security practices, such as enabling two-factor authentication, utilizing strong passwords, and keeping your wallet software up to date. Additionally, it is advisable to keep your private keys or seed phrases in a secure and offline location.
By taking these security measures, you can safely store and secure your SOL tokens, ensuring their availability and protecting them from unauthorized access.
The Future of Solana’s Consensus Mechanism
As Solana continues to grow and evolve, there are several upcoming improvements and updates to its consensus mechanism that aim to enhance its performance and capabilities.
Upcoming Improvements and Updates to Solana’s Proof-of-History
The Solana community and developers are actively working on further optimizing and refining the Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus mechanism. Ongoing research and development are focused on improving scalability, reducing or eliminating potential bottlenecks, and maintaining the network’s security.
By continuously enhancing PoH and incorporating new advancements, Solana aims to further solidify its position as a leading blockchain platform.
Potential Challenges and Limitations for Solana’s Consensus Mechanism
As with any technology, there are potential challenges and limitations that Solana’s consensus mechanism may encounter. These can include scalability limitations of the underlying infrastructure, potential vulnerabilities, or the need for regular updates and maintenance to address emerging risks.
To overcome these challenges, the Solana community and development team remain committed to continuous research, collaboration with the wider blockchain community, and implementing proactive security measures.
The future of Solana’s consensus mechanism relies on the dedication of its community, the support of developers, and the ability to adapt and evolve in response to emerging technologies and challenges.
Integration with Other Blockchain Projects
As Solana establishes itself as a leading blockchain platform, collaboration and integration with other blockchain projects become valuable and mutually beneficial. Solana’s compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) allows developers to leverage existing Ethereum applications and infrastructure while benefiting from Solana’s scalability and speed.
Moreover, Solana’s interoperability with other blockchains promotes the seamless transfer of assets and data, fostering a connected and decentralized ecosystem. Integration with emerging technologies and partnerships with industry leaders are crucial for Solana’s growth and progress.
Ultimately, the future of Solana’s consensus mechanism lies in its ability to adapt, collaborate, and provide innovative solutions for the evolving needs of the blockchain industry.
Case Studies and Success Stories in Solana
Solana has demonstrated its capabilities and potential through various case studies and success stories. Let’s explore some real-world examples where Solana’s consensus mechanism has been successfully implemented.
Real-World Examples of Solana’s Consensus Mechanism in Action
One notable example of Solana’s successful implementation is Serum, a decentralized exchange (DEX) built on the Solana blockchain. Serum leverages Solana’s high transaction speeds and low costs to provide users with a seamless and efficient trading experience.
The high-performance capabilities of Solana enable Serum to handle a large volume of transactions without congestion, offering users fast and reliable trading opportunities. This real-world application showcases the benefits of Solana’s consensus mechanism in the context of decentralized finance.
Successful Projects Built on Solana
Solana has fostered the development of various successful projects across different industries. For instance, Mango Markets provides users with a decentralized trading platform for spot and leveraged trading on Solana.
Other projects built on Solana include Raydium, a liquidity pool protocol, and Audius, a decentralized music streaming platform. These projects leverage Solana’s scalability, speed, and security to offer innovative solutions to users.
User Reviews and Feedback on Solana’s Performance
User reviews and feedback play a crucial role in assessing the performance and reliability of a blockchain platform. Solana has garnered positive feedback from developers, users, and industry leaders alike, praising its speed, scalability, and overall usability.
Users appreciate Solana’s transaction speeds, especially in comparison to other blockchain platforms. The low transaction costs and efficient infrastructure make it an attractive choice for applications that require high throughput and low-latency interactions.
Developers find Solana’s ecosystem to be robust, developer-friendly, and conducive to building complex decentralized applications. The availability of tools, resources, and documentation contributes to the positive developer experience on Solana.
Overall, user reviews and feedback attest to the reliability and performance of Solana’s consensus mechanism, positioning it as a promising blockchain platform with demonstrated success.
Conclusion
Solana’s Proof-of-History consensus mechanism, combined with its Delegated Proof-of-Stake mechanism, provides a powerful solution to the scalability, speed, and security challenges faced by traditional blockchain networks.
With its efficient use of timestamps, Solana achieves rapid transaction speeds, low costs, and enhanced security. These advantages make Solana well-suited for various use cases, including decentralized finance, smart contract development, and real-time data processing.
By obtaining and utilizing the SOL token, users can actively participate in the Solana network and benefit from its fast, scalable, and cost-effective infrastructure.
The future of Solana’s consensus mechanism holds exciting possibilities, with upcoming improvements, collaborations, and integration with other projects further enhancing its capabilities. Through real-world case studies and user feedback, Solana has proven its performance and reliability, positioning itself as a leading blockchain platform in the industry.
In conclusion, Solana’s Proof-of-History consensus mechanism offers a comprehensive solution to the scalability, speed, and security demands of the blockchain ecosystem, making it a promising choice for developers and users alike.